Our energy guide is aimed to help consumers understand more about the energy supplied to their residence.
The Basics
The Western Australian Government has made various laws and rules to regulate the energy industry. The Economic Regulation Authority (ERA) oversees some of these laws and is responsible for the licensing of energy suppliers. This guide will help you understand the energy industry and your rights and responsibilities as an energy customer.
Who does this guide apply to?
This guide applies to licensed retailers, licensed distributors and their customers. Licensed retailers and distributors hold a license issued by the ERA for the supply of energy.
Examples of licensed retailers include Synergy, Horizon Power and Kleenheat Gas.
Examples of licensed distributors include Western Power and ATCO Gas Australia. Some retailers and distributors, known as 'exempt,' operate without a license under State Government exemption.
Even if supplied by an exempt entity, you may still have some protection measures.
The information in this guide applies to small use customers. You are a small use customer if you use less than 160MWh (about $56,000) of electricity per year or up to 1TJ of gas per year (between $28,500 and $43,000, depending on where you live).
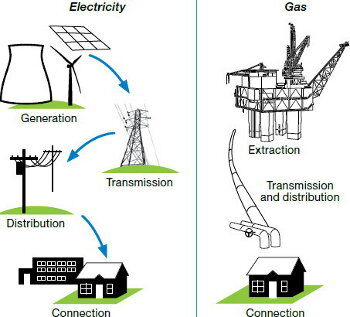
How energy is supplied to your property
Electricity is generated by generators, while gas is extracted from gas fields by producers. Transmission organisations transport this energy to distributors via high-voltage powerlines or high-pressure pipelines. Distributors own the low-voltage or low-pressure distribution networks that deliver energy to homes and businesses.
After forming contracts with electricity generators or gas producers for supply, retailers sell energy to residential & business customers. Retailers also contract with distributors for transportation and metering services, ensuring energy delivery and accurate measurement for homes and businesses.
The electricity industry
There are three major electricity networks in WA. These are the South West Interconnected System (SWIS), the North West Interconnected System (NWIS) and the Esperance System.
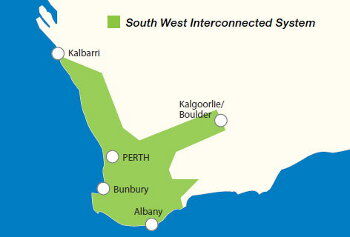
In 2022/23, over 1,062,000 residential electricty customers lived in the area supplied by the SWIS, compared to approximately 36,000 residential customers in other parts of the state.
Each network usually only has one distributor. This distributor may however transport electricity on behalf of several retailers. In the SWIS area, Western Power is the main licensed distributor and Synergy the largest licensed retailer. Horizon Power is the main licensed distributor and retailer for the area outside of the SWIS. Organisations can take on more than one supply role. For example, Horizon Power is a generator, transmitter, distributor and retailer.
Licensing the energy supply industry
Electricity generators, transmitters, distributors and retailers must have a licence issued by the ERA to supply electricity. Gas distributors and retailers who supply small use customers must also have a licence issued by the ERA. There are a few exceptions to this rule.
The ERA monitors licensed organisations to see if they comply with the conditions of their licences. When non-compliance is detected, the ERA may take action to make an organisation comply with the licence.
Who to contact and when?
As a customer, you only deal directly with your retailer or distributor. You do not have a direct relationship with other industry participants, such as generators.
Below is a list of the types of issues that you may need to contact a retailer or distributor about.
| Retailers | Distributors |
|---|---|
|
|
In addition to the ERA, there are other agencies that oversee the supply of energy. The main ones that you should be aware of are:
| Energy & Water Ombudsman |
|
|---|---|
| Energy Policy WA |
|
| EnergySafety |
|
How are energy prices set?
The price you pay for energy is made up of four costs:

Generation costs: costs to build generators or gas plants and generate electricity or extract gas.

Transmission costs: costs to build and maintain the high voltage power line or high pressure pipeline network.
Distribution costs: costs to build and maintain the network of pipes, low voltage poles and meters that deliver, measure and record energy to households and businesses.

Retail costs: costs to connect customers, provide customer service and manage accounts.
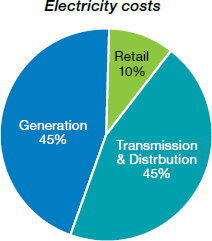
Energy prices
In the SWIS area, around 90% of your electricity bill covers generation, transmission, and distribution costs, with retail costs making up approximately 10%.
The State Government establishes maximum retail tariffs for Synergy, Horizon Power, and most gas retailers catering to small customers. These tariffs are set based on the amount that retailers must pay to purchase and transport the energy to their customers.
The ERA regulates the transmission and distribution cost component of some energy networks. The ERA does this by implementing access arrangements. These arrangements determine the amount of revenue that network owners may earn from retailers for the transportation of energy through their networks.
